Windows 10 and 11 (this also applies to older versions, such as Windows 8 and 8.1) have a built-in file indexer service. It is a sort of internal librarian that keeps track of all your files and folders on various drives. Indexing files in Windows improves the search speed and makes the operating system snappier.
Windows is a complex product with tens of thousands of lines of code. No wonder things sometimes go sideways, and random bugs appear, causing Windows Search Filter Host and Indexer high CPU load. When something consumes too much CPU resources, your computer slows down, heats up, and causes fans to spin much faster.
If you encounter the Microsoft Windows Search Filter Host high CPU load, this article will help you to fix search indexing problems on Windows 10, 11, and older versions.
Table of Contents
Windows Search Filter Host High CPU Load
Begin with checking the symptoms. You need to ensure that it is Windows Search Filter Host causes high CPU load. To do that, do the following:
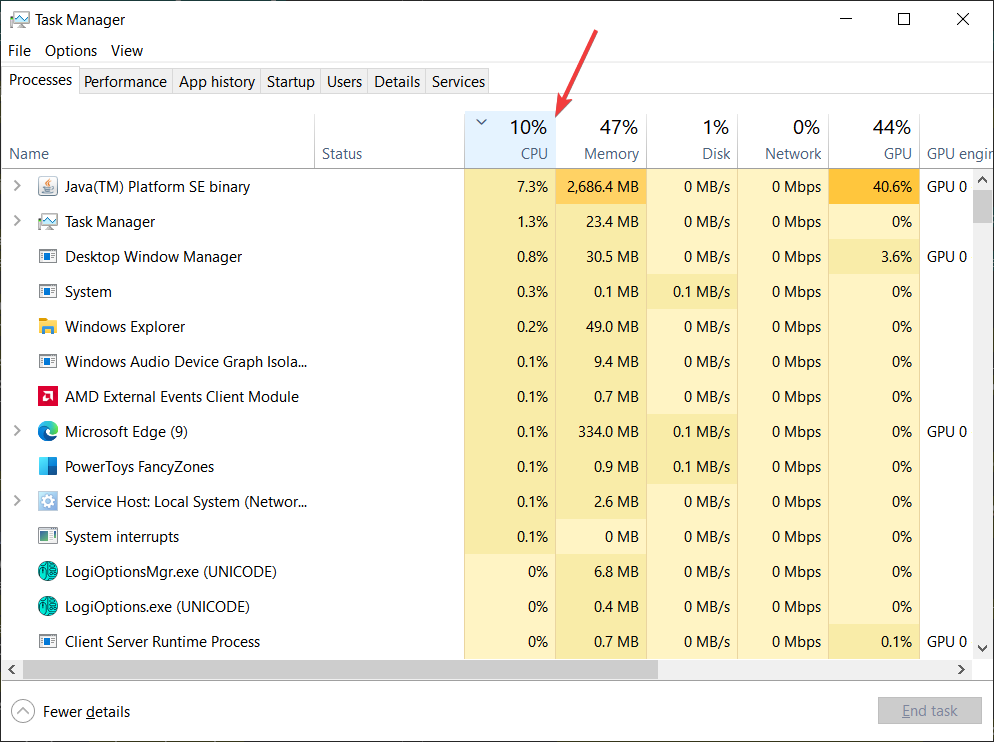
- Right-click the taskbar (on Windows 10) and select Task Manager. On Windows 11 you can right-click the Start menu button. Alternatively, press Ctrl + Shift + Esc. That shortcut works in every modern Windows version.
- On the Task Manager window, switch to the Processes tab.
- Next, click the CPU column to sort processes by the highest CPU load.
If Windows Search Filter Host causes high CPU load, you will see one of the following processes at the top of the list: Microsoft Search Protocol Host (SearchProtocolHost.exe executable), Microsoft Search Filter Host (SearchFilterHost.exe) or Microsoft Windows Search Indexer (SearchIndexer.exe or SearchUI.exe).
As you can see, in our case, the “Microsoft Windows Search Indexer” process uses more than 30% of the CPU and 3.2GB of RAM. That is not normal. In a properly working system, that process rarely uses more than 3% of the CPU and 100 MB of memory.
How to Fix Search Filter Host and Indexer High CPU Utilization on Windows 10?
The “Microsoft Windows Search Filter Host” and “Microsoft Windows Search Indexer” processes simplify the search inside Windows. These processes are a part of the system-wide “Windows Search” service responsible for scanning the file system, finding files, folders, apps, system utilities, and other parts of Windows you might need. All the information Microsoft Windows Search Indexer finds when straining your CPU is stored in a special database file (index DB).
As a part of normal operation, Windows indexes the following: names and paths to your files, creation time, keywords (document, text file or html-page), properties, and other data. When you perform a search from the Start Menu, Taskbar or Cortana in Windows 10, the operating system does not go through the entire drive. Instead, it refers to a structured index database. As the result, Windows returns the search results much faster.
When Microsoft Windows Search Filter Host consumes much CPU and RAM, that means the operating system is currently running the indexing service and working intensively on gathering information about your files and rebuilding the search index. Before you try to fix Microsoft Windows Search Protocol Host high CPU load, try to wait 20-30 minutes, so that Windows can complete the indexing process.
Of course, sometimes you cannot wait. If you critically need to reclaim the lost performance, try ending the Windows Search Filter Host process. Do not worry, it is safe. After all, Windows will restore the process in due time without your intervention.
- Launch the Task Manager.
- On the Processes tab, find the misbehaving process that takes too much CPU and RAM resources.
- Select the process, then click End Task.
If you do not use search features in Windows 10, you can disable the Windows Search Indexing service and prevent it from auto start.
- Press Win + R and enter the services.msc command.
- In the list of services, find the Windows Search service.
- Right-click Windows Search and select Stop (if available). Skip this step if the Stop action is not available.
- Next, double-click the service and change the Startup type parameter to Disabled.
- Click Ok to save changes.
- Although not necessary, restart your computer.
Note. Read our tutorial on how to fix an RDP connection error This computer can’t connect to the remote computer.
Fix Windows Search Filter Host and Indexer High CPU Load Using Search Troubleshooter
You can fix problems with the Search service in Windows using the built-in tool called “Indexing Troubleshooter.” You can run Windows Search Indexing Troubleshooter by doing the following:
- Press Win + I to open the Windows Settings app.
- Go to Search > Searching Windows.
- Scroll down the list of option and click the Run the indexer troubleshooter to resolve common search issues link.
- Alternatively, use the following command: msdt.exe -ep WindowsHelp id SearchDiagnostic.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to fix Windows Search Filter Host and Indexer High CPU load in Windows.
How to Rebuild the Search Index Database in Windows?
For many, disabling Windows Search Indexer to fix high CPU loads is not the option. In such a case, try rebuilding the Windows Search Indexer database.
- Press Win + R and enter the control command.
- Switch the view to Large Icons or Small Icons.
- Open the Indexing Options section.
- Now you need to modify how the indexer works. Click the Modify button.
- Uncheck all options that you do not need to index.
- Next, go to Advanced indexing.
- Click the Rebuild button.
- Windows will show you the following message:
Rebuilding the index might take a long time to complete. Some view and search results might be incomplete until rebuilding is finished.
- Click OK.
Once Windows finishes rebuilding the indexing database, use your computer as you usually do. Monitor how the system uses CPU resources to spot misbehaving processes. The Search Protocol Host and Search Filter Host processes should be causing much lower CPU load.
As another option, you can temporarily stop the system indexing by suspending the Windows Search service for 15 minutes. To do so, go to the Indexing Options in the Control Panel and press the Pause button.
This may be a preferrable option when the SearchFilterHost process prevents you from working properly, but you do not want to disable indexing services.
In some cases, it is more efficient not to rebuild the index database. Instead, remove the index database file. To do so, open Command Prompt with elevated privileges (run as Administrator) and execute the following commands:
net stop WSearch rd C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Search /s /q net start WSearch
If these methods did not help you to fix the Windows Search Filter Host and Indexer High CPU Load problem, run the Windows 10 Troubleshooter from Control Panel > Troubleshooting > View all > Search and Indexing. Follow the on-screen instructions.
In some cases, users fixed the search problem by disabling the Bing Search feature (can used by Windows 10 for local search processes). You can do this by changing the value of the registry parameter BingSearchEnabled from 0 to 1. To do so, launch the Command Prompt as Administrator and execute the following command:
reg.exe add HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Search /v BingSearch
We hope this article helped you fix the Windows Search Filter Host and Indexer High CPU Load problem and reclaim the lost performance.