Simple Network Management Protocol or SNMP is used for monitoring, event notification, and network device management on corporate networks. The protocol consists of a set of network management standards, including the Application Layer protocol, database schemas, and a set of data objects. SNMP can receive various types of information (uptime, performance counters, device parameters, etc.) from any network device. SNMP can receive information from switches, servers, routers, or computers on which the SNMP agent is installed. In Windows 10 and Windows 11, the SNMP service is available as a separate Windows feature and isn’t installed by default.
Table of Contents
Installing SNMP Service on Windows 11
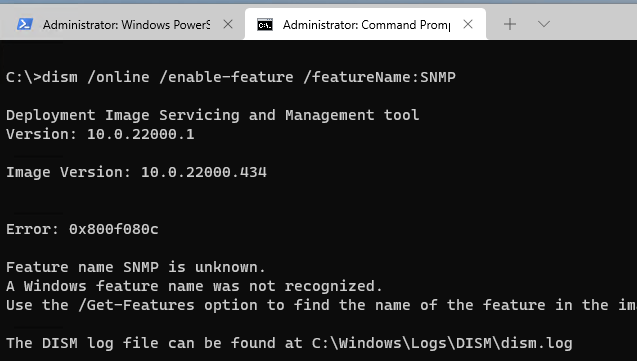
In previous versions of Windows (Win 8.1, 7, or 10 RTM), it was possible to install the Windows SNMP service via Control Panel > Add Program and Features applet or using the DISM command:
dism /online /enable-feature /featureName:WMISnmpProvider
However, on Windows 11, when you run this command, you get an error:
Error: 0x800f080c
Feature name WMISnmpProvider is unknown.
A Windows feature name was not recognized.
Use the /Get-Features option to find the name of the feature in the image and try the command again. A Windows feature name was not recognized.
Also, Microsoft deprecated SNMP from Control Panel > Add Program and Features applet.
On Windows 11, you can still install the SNMP client and WMI SNMP Provider services, however, Microsoft has changed the install ways.
Note. Learn how to configure the Lock Screen in Windows.
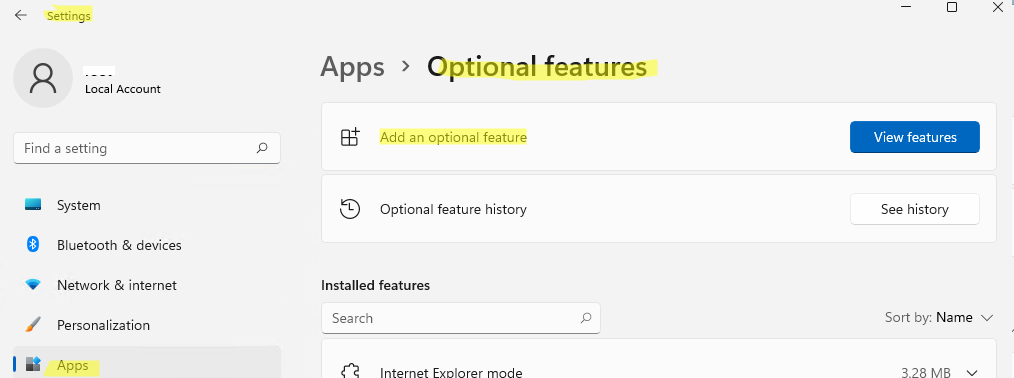
The SNMP service in Windows 11 can be installed via the Settings app:
- Right-click Start > Settings > Apps > Optional Features > Add an optional feature > View features;
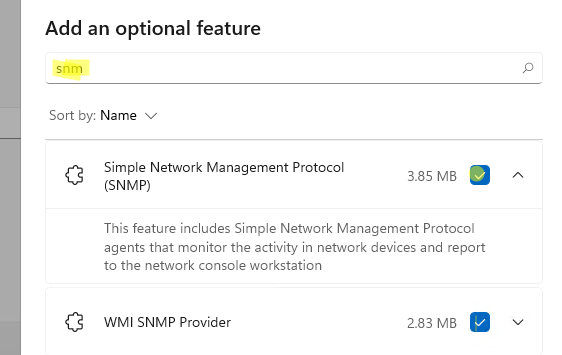
- Type SNMP in the search field and select Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and WMI SNMP Provider (optional) to install;
- Click Next > Install;
- To install the components, your computer must be connected to the Internet. An error will appear when installing the SNMP feature if the computer is offline or located on a disconnected network.
You can also install the SNMP service on Windows 11 using PowerShell:
- Open Windows Terminal as an administrator;
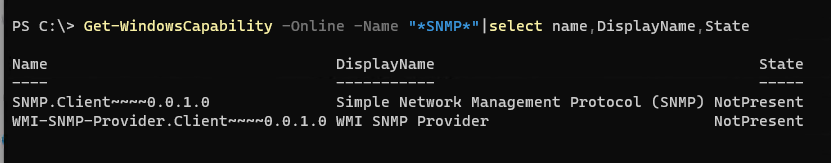
- Check if the SNMP service is not installed (State=NotPresent):
Get-WindowsCapability -Online -Name "*SNMP*"|select name,DisplayName,State
- To install the SNMP service, run the command:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name “SNMP.Client~~~~0.0.1.0“
- In order to install WMI SNMP Provider, run the command:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name "WMI-SNMP-Provider.Client~~~~0.0.1.0"
- Wait for the installation to finish and check the SNMP feature state again using the Get-WindowsCapability cmdlet. The state should change to Installed.
How to Install SNMP Service in Windows 10?
In earlier Windows 10 builds (1803-), it was possible to install the SNMP service via Control Panel > Programs and Features > Turn Windows features on or off. Select Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and the WMI SNMP Provider (provides access to the SNMP information via the Windows Management Instrumentation interfaces), and click OK.
In modern Windows 10 builds (22H2, 22H1) you should use PowerShell or the Settings pane to install the SNMP service as Feature on Demand (FoD).
If your computer has a direct Internet connection, you can install the SNMP service components online from Microsoft servers. To do this, open the elevated PowerShell console and run the command:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name "SNMP.Client~~~~0.0.1.0"
You can also use DISM to install the SNMP service and WMI provider:
DISM /online /add-capability /capabilityname:SNMP.Client~~~~0.0.1.0
DISM /online /add-capability /capabilityname:WMI-SNMP-Provider.Client~~~~0.0.1.0
After that, you can verify if the SNMP service is installed:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online -Name "SNMP*"
Name : SNMP.Client~~~~0.0.1.0
State : Installed
DisplayName : Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Description : This feature includes Simple Network Management Protocol agents that monitor the activity in network devices and reports it to the network console workstation
DownloadSize : 595304
InstallSize : 1128133
To disable the SNMP service, use the PowerShell command:
Remove-WindowsCapability -Online -Name "SNMP.Client~~~~0.0.1.0"
You can also install the SNMP service through the Optional Features graphical interface.
Go to the Settings > Apps > Apps & Features > Manage optional feature > Add Feature. Select the following features in the list: Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and WMI SNMP Provider (to get all SNMP service configuration tabs).
After that, the SNMP service will appear in the services.msc console.
You can check if the SNMP service is installed on your Windows 10 by using the PowerShell Get-Service cmdlet:
Get-Service -Name snmp*
Note. Microsoft plans to completely remove the SNMP service in the next Windows builds because of the security risks associated with this protocol. Instead of SNMP, it is recommended to use the Common Information Model (CIM), which is supported by Windows Remote Management.
Fixing Error 0x800f0954 When Installing SNMP on Windows 10 or 10
In Windows 10 and 11, SNMP is a part of the Feature on Demand (FoD) concept, which requires a direct connection to Microsoft’s online update servers. You may receive error 0x800f0954 when installing SNMP components if your computer is on an isolated segment or corporate network:
Add-WindowsCapability failed error. Error code = 0x800f0954
This error will appear if your computer is on a corporate network and is configured to receive Windows updates from an internal WSUS server (Windows Server Update Services). The computer is trying to download SNMP binaries from the WSUS server instead of the Microsoft Update servers.
You can change the settings of computers so that they receive optional feature files directly from Windows Update instead of from WSUS. This requires the following GPO setting to be configured on the Windows client:
- Open the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc);
- Then navigate to the Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System;
- Enable the GPO option Specify settings for optional component installation and component repair and check the box Download repair content and optional features directly from Windows Updates instead of Windows Server Updates Services (WSUS);
- Update the Group Policy settings on a computer:
gpupdate /force
Now restart the Windows Update service:
Get-Service wuauserv| Restart-Service -Force
You can now use PowerShell or Settings to install any Windows optional feature. The binaries that you need will be automatically downloaded from Windows Update.
If your computer is in a disconnected environment (without Internet), you can install SNMP using the offline FoD ISO image. You can download the FOD media from your Volume License Servicing Center (VLSC).
Mount the ISO image to a virtual DVD drive (for example, E:), and install SNMP using the PowerShell command:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SNMP -Source "E:\Sources\sxs"
Enable SNMP Service on Windows Server
Now let’s see how to install SNMP service and WMI providers on Windows Server 2022/2019/2016.
SNMP is not installed on Windows Server by default. You can install the service in one of the following ways:
- Via the Server Manager: Add roles and Features > Features > SNMP service (you can also check SNMP WMI Providers).
- Using PowerShell:
Install-WindowsFeature SNMP-Service,SNMP-WMI-Provider –IncludeManagementTools
Configure SNMP Service on Windows Computer
After the installation, SNMP services should start automatically. Open the Services management console (services.msc). Two new services should appear in the service list:
- SNMP Service — this is the primary SNMP agent service, that tracks activity and sends information;
- SNMP Trap — receives trap messages from local or remote SNMP agents, and forwards messages to the SNMP management software that is being run on that computer.
Open the properties of the SNMP Service. If it is stopped, restart it by pressing the Start button and then changing the startup type to Automatic.
Click the Agent tab. Fill in the Contact and Location fields (you can specify the user’s contact name and computer location). Then select the list of services from which you want to collect data and send it to the monitoring device. There are five service-based options:
- Physical;
- Applications;
- Internet;
- End-to-end;
- Datalink and subnetwork.
Click the Security tab. Here you can configure various security settings for your SNMP servers.
The list of Accepted community names contains the names of the communities whose SNMP hosts are authenticated to send SNMP requests to this computer. The community name has the same functions like login and password.
Click the Add button and specify the Community Name and one of the five access levels (None, Notify, READ ONLY, READ WRITE, READ CREATE). READ WRITE is the maximum access level at which the SNMP management server can make changes on the system. For monitoring systems, it is usually enough to select READ ONLY (the monitoring server can only poll the system, but not make changes). In our example, we added a community name public with READ ONLY permissions.
Add a list of monitoring servers (IP addresses) to the Accept SNMP packets from these hosts from which you want to accept SNMP packets. This could be your monitoring system, for example, Zabbix, Nagios, Icinga, OpenNMS, PRTG, and Microsoft System Center Operations Manager (SCOM).
Tip. You can select the Accept SNMP packets from any host option. In this mode, the SNMP agent accepts packets from any host without restrictions. This option is not recommended for use on public computers. This is not safe.
Save the changes and restart the SNMP service.
Hint. To make your Windows host receive and send SNMP queries and traps, you need to open SNMP ports in Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security. SNMP uses UDP as a transport protocol. Two ports are used: UDP 161 (SNMP) and UDP 162 (SNMPTRAP). You can open inbound and outbound SNMP ports in Windows Firewall using the following commands:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="SNMP UDP Port 161 In" dir=in action=allow protocol=UDP localport=161
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="SNMP UDP Port 161 Out" dir=out action=allow protocol=UDP localport=161
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="SNMPTRAP UDP Port 162 In" dir=in action=allow protocol=UDP localport=162
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=" SNMPTRAP UDP Port 162 Out" dir=out action=allow protocol=UDP localport=162
Configuring SNMP Settings via Group Policy
Several GPO parameters will help you configure SNMP parameters centrally. These parameters are located in the GPO editor (gpedit.msc or gpmc.msc) under Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates definitions > Network > SNMP.
Three SNMP policy parameters are available:
- Specify communities — allows you to set a list of communities for the SNMP service;
- Specify permitted managers — allows you to specify a list of permitted hosts that can send SNMP queries to the agent on this computer;
- Specify traps for public community — allows you to set up trap configuration for the Simple Network Management Protocol.
Another way to configure SNMP parameters is through the registry. These parameters are set in the following section of the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\SNMP\Parameters.
You can configure SNMP parameters as needed on a reference computer, export them to a REG file, and deploy the REG file to servers/computers via GPO (Computer Configuration > Preferences > Windows Settings > Registry).
You can use SNMP and SNMP Traps to monitor different metrics of your Windows device (uptime, CPU usage, RAM, storage, network traffic). The Windows SNMP service currently supports only SNMP v1 and SNMP v2c. These protocols are not encrypted. It means that an attacker can intercept all your SNMP data and view it in plain text. Windows 10 and 11 do not support SNMP v3 which is an encrypted and more secure protocol.
This completes the SNMP service configuration in Windows. If you need to enable SNMP on multiple computers or servers, you can remotely install and configure the SNMP service using PowerShell or Group Policy.












4 comments
Good job with this great article. You have saved me with testing a system monitoring light board program.
Thank you for your excellent explanations of his lines of code on SNMP.
For the field “Accept SNMP packets from these hosts”, I have never seen a hostname work here. Only IP address works. That is, this window will accept either hostname or IP, but the desired effect only is achieved using IP address(es).
Hello, how can I install SNMP on windows 10 machine without internet?
Comments are closed.